Population vs Sample in Research
In research, statistics consist of numerical data and data sets. Populations and samples are two types of statistical data sets.
Difference between Population and Sample
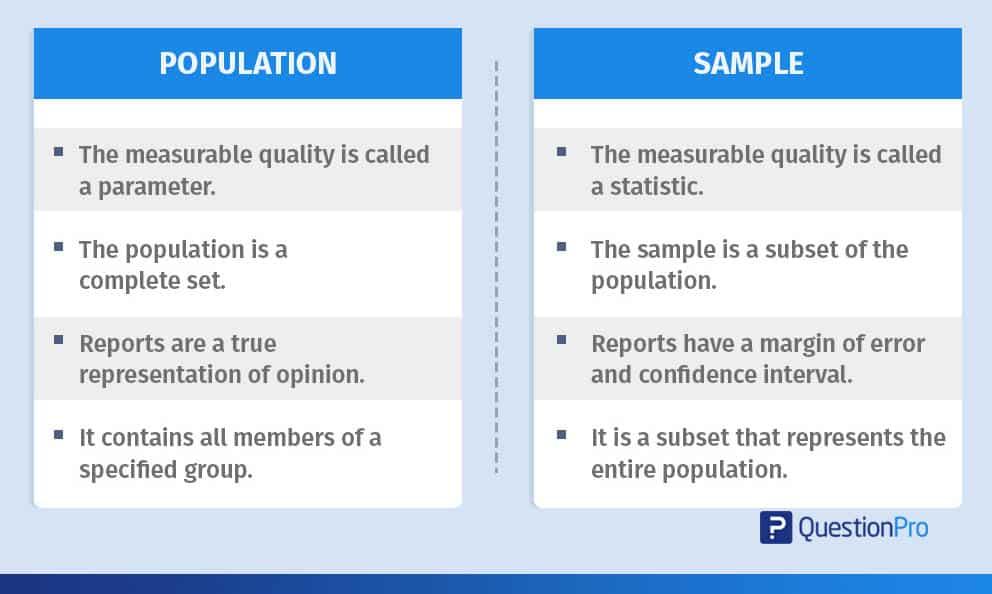
Population
What is a population? In a statistical or quantitative methodology study, the population is a well-defined whole set of items from which data are drawn.
- The members of a population possess a common trait and/or behavior. Some of the things a population can consist of are a group of individuals, events, objects, or organizations.
- The population represents the entire group of individuals or objects that the researcher wants to generalize about in the study’s findings.
- For example, a researcher wants to investigate visitors’ opinions about the Sea World in San Antonio, TX. The population would be all the people who visit that Sea World location.

Sample
What is a sample? A sample is a smaller representation and subset of a larger population. When the population size in a study is too large for all members to be included, a sample is used to investigate the behavior or characteristics of the entire population data.
- The results obtained for the sample in the study can be used to generalize about the entire population.
- The accessible population is a subset of the larger population and is the part that the researcher has access to and can feasibly include in the study.
- For example, for the researcher who wants to investigate visitors’ opinion about the Sea World in San Antonio, TX. The sample could be a group of 20-25 high school teenagers from San Antonio, TX who visit Sea World as part of their school’s field trip each month.
The following represents a summary of the differences between the population and the sample:
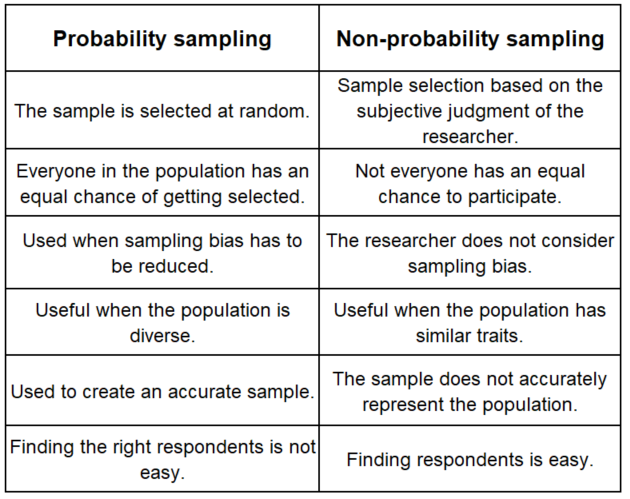
Probability Sampling and Non-probability Sampling
Random samples of data are obtained using probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling is done randomly and ensures that each member of the research population has an equal chance of being a part of the study’s sample.
In non-probability sampling, the population members do not have an equal chance of being a part of the study. The sample group that is selected is based on the researcher’s subjective judgment rather than randomly. This could be because they are conveniently available, or they were referred as suitable participants. The following represents a summary of the differences between probability non-probability sampling.
Examples of Populations
- All the hardware stores in a 30-mile perimeter
- Seniors at Harvard University
- All teenagers with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Workers at Starbucks
Examples of Samples
It is necessary that the sample is representative of the population. If it is not, the sample is considered biased, and will produce results that are invalid and inaccurate.
- The hardware stores in a 30-mile perimeter that are open seven days a week and also deliver
- Female graduating seniors at Harvard University who have a GPA of 3.7 or higher in 2023
- High school male teenagers in the metropolitan Vidalia, GA area who have attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Baristas at Starbucks in Sheridan, WY who are 30 years and older with two or more years of experience.
Note: For more information, review the following websites:
freeCodeCamp website: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/population-vs-sample-statistics-example/
Statology.org website: https://www.statology.org/population-vs-sample/
 Waiting to Get Your Dissertation Accepted?
Waiting to Get Your Dissertation Accepted?






